Surface Areas and Volumes Mind Maps
Surface Areas and Volumes of Solids
(i) Cuboid:
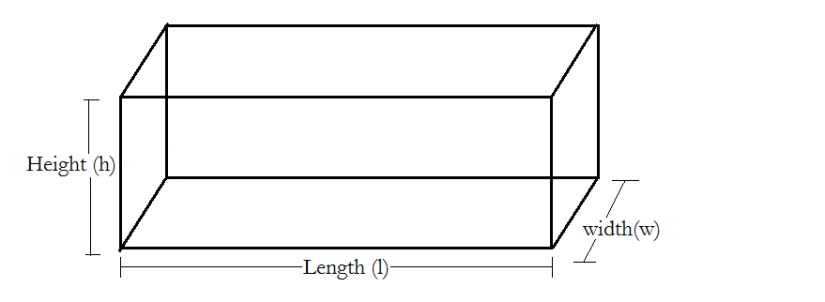
Volume = l × b × h
Total surface area = 2 [lb + bh + hl]
Lateral surface area = 2 [bh + hl]
Diagonal of the coboid =
(ii) Cube:
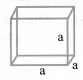
Volume = a3
Total surface area = 6a2
Lateral surface area = 4a2
Diagonal of a cube = √3a
(iii) Cylinder:
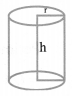
(a) Right circular cylinder:
Volume = πr2h
Curved Surface Area = 2nrh
Total Surface Area= 2πrh + 2πr2 = 2πr(r + h)
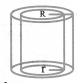
(b) Right circular hollow cylinder:
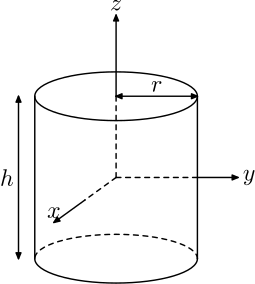
Let r and R be internal & external radii.
Volume = n(R2 – r2)h
Curved Surface Area = 2π(R + r)h
Total Surface Area = 2π(R + r)h + 2π(R2 – r2)
= 2π(R + r)(h + R — r)
(iv) Right circular cone:
Slant height, l = 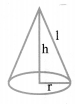
Volume =
Curved Surface Area = πrl
Total Surface Area = πrl + πr2
Surface Areas and Volumes of Sphere and Hemisphere
(i) Sphere:
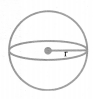
Volume =
Surface area =4πr2
(ii) Hemisphere:

Volume =
C.S.A = 2πr2
T.S.A = 3πr2
(iii) Hemispherical shell:
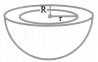
Volume =
Curved Surface Area = 2π(R2 + r2)
Total Surface Area = 2π(r2 + R2) + n (R2 – r2)
= π (r2 + 3R2)
Surface Areas of a Combination of Solids
The surface area of a solid which is a combination of two or more solids is calculated by adding the surface areas of the individual solids which are visible in the new solid formed.
For Example: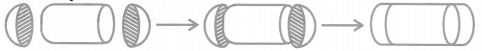
If we consider the surface of the newly formed object as given in the figure above, we would be able to see only the curved surfaces of the two hemispheres and the curved surface of the cylinder.
So, the total surface area of the new solid is the sum of the curved surface areas of each of the individual parts. This gives, TSA of new solid = CSA of one hemisphere + CSA of cylinder + CSA of other hemisphere
Volume of a Combination of Solids
Whenever solid is formed by combining two or more solids, then the amount of matter present in the new solid is equal to the sum of amounts of matter in the constituting solids. Volume of new solid = sum of the volumes of the individual solids
Conversion of Solid form One Shape to Another
(i) When a solid is converted from one shape to other, then its volume remains same only its shape and size changes.
(ii) If a solid is converted into a number of small identical solids, then Number of small items
Frustum of a Cone [Very Important for Board Exam]
When we slice (or cut) through a cone with a plane parallel to its base (see below figure ) and remove the cone that is formed on one side of that plane, the part that is now left over on the other side of the plane is called a frustum of the cone.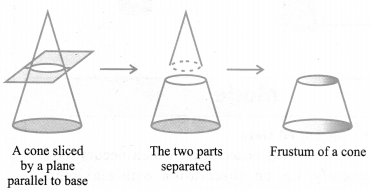
(i) Volume of the frustum of cone
(ii) C.S.A. of the frustum of cone = π(r1 + r2)l,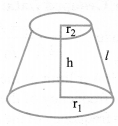
where l =
iii) T.S.A. of the frustum of cone
l =

No comments:
Post a Comment